D
Deleted member 952
Guest
Hi,
What drive format do you guys use for windows 11, REFs or NTFS or any other format?
Thanks
What drive format do you guys use for windows 11, REFs or NTFS or any other format?
Thanks
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
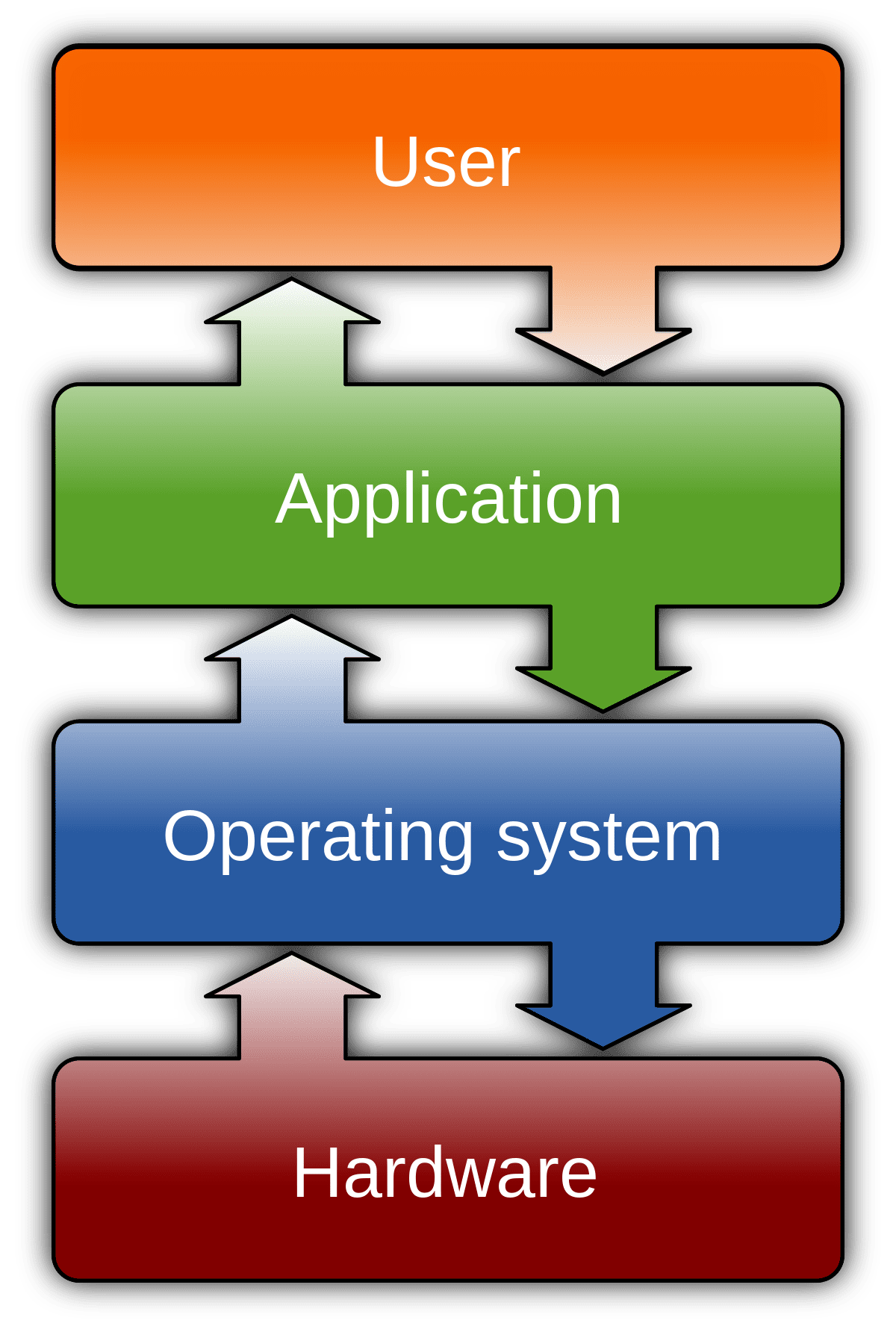
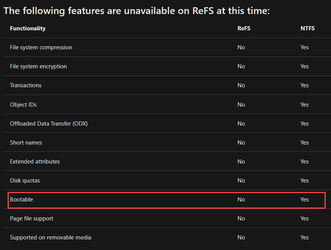
Again, ReFS is no longer an option. It was removed starting with the 2017 Fall Creator's Update of Windows 10 except in Pro for Workstations and Enterprise editions. You can still read ReFS partitions, but cannot create them. Also, in those OS versions and editions that support ReFS, you cannot install Windows on an ReFS partition.Read a lot on REFs recently and I think I'll pick NTFS even though REFs is newer technology. Resilient File System (ReFS) overview

NTFS's compatibility with other OSes isn't as good as exFAT, not to mention the clustersizes can be set much higher on the letter. Useful if you've got a drive dedicated to large files.As I said, why bother? Just forget it and keep using NTFS
"there are reasons to use formats other than NTFS" =/= "there are reasons for you, personally, to use NTFS"I hardly use another OS besides Windows, so I don't care. If I ever need to access an NTFS disk from Linux or Android or Mac OS I run the appropriate commands to enable full NTFS access and use it like a native disk.
Showing gratitude is important in online communities. Use the "like" button to appreciate helpful content. This motivates people to keep sharing knowledge. A "like" gives 1 point, "Helpful" gives 5 points, and "Great support" gives 10 points for exceptional help.
