- Local time
- 7:14 AM
- Posts
- 870
- OS
- Windows 11, Windows 10, Linux Fedora Cinnamon
Please do not follow these instructions without suitable guidance otherwise you can end up with an unbootable machine. Please read the final section for instructions on how to overcome this if this does happen.
Please do not follow the Driver Verifier tutorial written for Windows 10 which is available on Ten Forums. This tutorial is not suitable for general use for reasons which will be explained in the "Problems with I/O Verification" section. It is not a "safer" option; in fact, it is more likely to cause you unrelated crashes which will muddle our troubleshooting efforts.
Driver Verifier is a very useful troubleshooting tool when used correctly, however, these instructions should only be followed with the supervision of an experienced analyst. They have been written with Windows 11 machines in mind and therefore some of the settings may have been excluded due to deprecation from Microsoft. The general recommendation is to run Driver Verifier for between 24-48 hours or until a Driver Verifier related crash is thrown. These are the following:
- STOP 0xC1: SPECIAL_POOL_DETECTED_MEMORY_CORRUPTION
- STOP 0xC4: DRIVER_VERIFIER_DETECTED_VIOLATION
- STOP 0xC6: DRIVER_CAUGHT_MODIFYING_FREED_POOL
- STOP 0xC9: DRIVER_VERIFIER_IOMANAGER_VIOLATION
- STOP 0xD6: DRIVER_PAGE_FAULT_BEYOND_END_OF_ALLOCATION
- STOP 0xE6: DRIVER_VERIFIER_DMA_VIOLATION
Step 1: Please create a suitable restore point or back up image. This will make it easier to revert back to a working system in case you run into any difficulties such as a BSOD boot loop from running Driver Verifier. This is usually caused by a boot driver throwing a bugcheck exception while Driver Verifier is running.
Step 2: Please search for "verifier" from the Start Menu and then accept the UAC prompt if presented with one. You should see a screen which looks like the following:
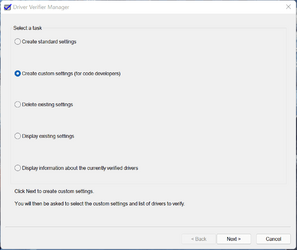
Please select the option called "Create custom settings (for code developers)". This will allow us to select the recommended tests to verify the drivers against.
Step 3:
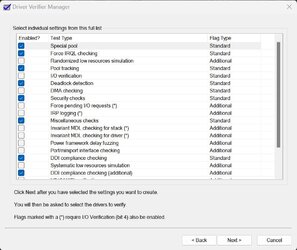
Please enable the settings shown above, that means enable the following:
- Special Pool
- Force IRQL Checking
- Pool Tracking
- Deadlock Detection
- Security Checks
- Miscellaneous Checks
- DDI Compliance Checking
- DDI Compliance Checking (Additional)
Problematic Settings:
- Power Framework Delay Fuzzing
- Kernel Synchronisation Delay Fuzzing
Additionally, please do not, under any circumstances, enable "Randomised Low Resources Simulation" as it is known to cause false positives and is generally not needed at all.
Source:Driver Verifier fails random instances of the driver's memory allocations, as might occur if the driver was running on a computer with insufficient memory. This tests the driver's ability to respond properly to low memory and other low-resource conditions.

Moreover, please do not enable "Systematic Low Resources Simulation" as it is known to cause false positives and can make the system generally unresponsive. It is even not recommended by Microsoft unless you're testing a very specific set of drivers.
Source: Systematic low resources simulation - Windows driversCaution This option is not intended for use when you are verifying all (or a large collection of) drivers on a computer. This option should be used only when you are doing targeted testing of individual drivers or their attached filter drivers. Using this option on a large number of drivers at the same time could cause unpredictable results, and could force crashes in components unrelated to the driver(s) you are testing.
Problems with I/O Verification:
1. The I/O verification option is designed to test for a particular set of bugs which we do not usually encounter when troubleshooting crashes. More importantly, this option should only be enabled on one driver at a time, in order to maximise it's effectiveness. This is officially stated in the Microsoft documentation here:
Source: I/O Verification - Windows driversWhen Level 1 I/O Verification is enabled, all IRPs obtained through IoAllocateIrp are allocated from a special pool and their use is tracked.
[...]
Because the special IRP pool is of limited size, I/O Verification is most effective when it is only used on one driver at a time.
2. The other two options rely on I/O Verification being enabled, however, IRP Logging simply creates an additional log which is only really useful for Stop 0x44 bugchecks. The other option which is "Force Pending I/O Requests" shouldn't even be enabled unless you have the source code associated to the driver you're testing:
Source: Force Pending I/O Requests - Windows driversCaution Do not use this option on a driver unless you have detailed knowledge of the operation of the driver and have verified that the driver is designed to handle STATUS_PENDING return values from all of its calls to IoCallDriver. Running this option on a driver that is not designed to handle STATUS_PENDING from all calls can result in crashes, memory corruptions, and unusual system behavior that can be difficult to debug or correct.
Step 4:
Once you've selected the settings, you're now ready to select the drivers which you wish to verify. To do so, please select the option titled "Select driver names from a list" and then sort all the drivers by the Provider column. Please select all the drivers apart from those listed as "Microsoft".
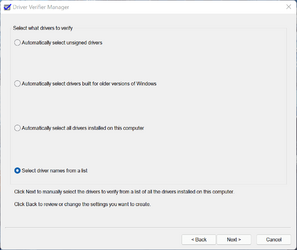
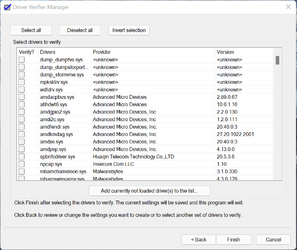
We generally do not recommend testing Microsoft drivers with the exception of the following:
- ndis.sys
- fltmgr.sys
- storport.sys
- wdf01000.sys
I would also recommend not enabling verification on any drivers prefixed with dump_ or hiber_ since these drivers are responsible for managing dump and hibernation file creation, as mentioned here: What are these ghost drivers named dump_diskdump.sys and other dump_*.sys that didn't come from any file? - The Old New Thing
Once you've selected the desired drivers then select Finish and then reboot the computer to start Driver Verifier.
You do not need to continuously enable and disable different settings on different subsets of drivers in order to "catch" a driver. Just enable Driver Verifier with the above settings and the recommended driver verification list and let it run. Although, please take into consideration a very important point: Driver Verifier is only designed to test for a specific set of common programming bugs and therefore if it doesn't crash, then it doesn't necessarily mean that your BSODs are being not caused by problematic drivers.
Verifying Driver Verifier Settings:
To ensure that it is running then you can open an elevated (administrative) command prompt and enter the following command:
verifier /queryIf Driver Verifier has been successfully started, then you should see the settings list of which options have been enabled. Otherwise, you’ll get a message indicating that no drivers are currently being verified.
To disable Driver Verifier, then please open an elevated command prompt and enter the following command:
verifier /resetYou will need to reboot the machine.
Disabling Driver Verifier (Boot Loop):
To disable Driver Verifier outside of Windows, then you will need to enter the Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE) and then open command prompt. From there, you will need to load your SYSTEM hive using the following command:
reg load HKLM\LIVESYSTEM C:\Windows\System32\config\SYSTEMYou can use any alias for the SYSTEM hive, as long as, it is not SYSTEM as a temporary version intended just for the recovery environment has already been loaded. Once the hive has been successfully loaded, then enter the following commands:
reg delete "HKLM\LIVESYSTEM\ControlSet00#\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management" /v VerifyDrivers /f
reg delete "HKLM\LIVESYSTEM\ControlSet00#\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management" /v VerifyDriverLevel /fThe control set number will vary between different machines but it will be mapped to your current control set, which you can find by querying the the following key:
reg query HKLM\LIVESYSTEM\Select /v CurrentIf the command returned 1 for example, then the current control set would be ControlSet001. Once you have deleted the appropriate values then unload the SYSTEM hive and reboot the system.
reg unload HKLM\LIVESYSTEMThe VerifyDrivers value simply contains a list of all the drivers which are being verified, whereas, the VerifyDriverLevel is a bitwise flag for the settings which have been enabled.
- Windows Build/Version
- Windows 11
My Computer
System One
-
- OS
- Windows 11, Windows 10, Linux Fedora Cinnamon