Microsoft On the Issues:
As we enter a new era based on artificial intelligence, we believe this is the best time to articulate principles that will govern how we will operate our AI datacenter infrastructure and other important AI assets around the world. We are announcing and publishing these principles – our “AI Access Principles” – today at the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona in part to address Microsoft’s growing role and responsibility as an AI innovator and a market leader.
Like other general-purpose technologies in the past, AI is creating a new sector of the economy. This new AI economy is creating not just new opportunities for existing enterprises, but new companies and entirely new business categories. The principles we’re announcing today commit Microsoft to bigger investments, more business partnerships, and broader programs to promote innovation and competition than any prior initiative in the company’s 49-year history. By publishing these principles, we are committing ourselves to providing the broad technology access needed to empower organizations and individuals around the world to develop and use AI in ways that will serve the public good.
These new principles help put in context the new investments and programs we’ve announced and launched across Europe over the past two weeks, including $5.6 billion in new AI datacenter investments and new AI skilling programs that will reach more than a million people. We’ve also launched new public-private partnerships to advance responsible AI adoption and protect cybersecurity, new AI technology services to support network operators, and a new partnership with France’s leading AI company, Mistral AI. As much as anything, these investments and programs make clear how we will put these principles into practice, not just in Europe, but in the United States and around the world.

These principles also reflect the responsible and important role we must play as a company. They build in part on the lessons we have learned from our experiences with previous technology developments. In 2006, after more than 15 years of controversies and litigation relating to Microsoft Windows and the company’s market position in the PC operating system market, we published a set of “Windows Principles.” Their purpose was to govern the company’s practices in a manner that would both promote continued software innovation and foster free and open competition.
I’ll never forget the reaction of an FTC Commissioner who came up to me after I concluded the speech I gave in Washington, D.C. to launch these principles. He said, “If you had done this 10 years ago, I think you all probably would have avoided a lot of problems.”
Close to two decades have gone by since that moment, and both the world of technology and the AI era we are entering are radically different. Then, Windows was the computing platform of the moment. Today, mobile platforms are the most popular gateway to consumers, and exponential advances in generative AI are driving a tectonic shift in digital markets and beyond. But there is wisdom in that FTC Commissioner’s reaction that has stood the test of time: As a leading IT company, we do our best work when we govern our business in a principled manner that provides broad opportunities for others.
The new AI era requires enormous computational power to train, build, and deploy the most advanced AI models. Historically, such power could only be found in a handful of government-funded national laboratories and research institutions, and it was available only to a select few. But the advent of the public cloud has changed that. Much like steel did for skyscrapers, the public cloud enables generative AI.
Today, datacenters around the world house millions of servers and make vast computing power broadly available to organizations large and small and even to individuals as well. Already, many thousands of AI developers – in startups, enterprises, government agencies, research labs, and non-profit organizations around the world – are using the technology in these datacenters to create new AI foundation models and applications.
These datacenters are owned and operated by cloud providers, which include larger established firms such as Microsoft, Amazon, Google, Oracle, and IBM, as well as large firms from China like Alibaba, Huawei, Tencent, and Baidu. There are also smaller specialized entrants such as Coreweave, OVH, Aruba, and Denvr Dataworks Corporation, just to mention a few. And government-funded computing centers clearly will play a role as well, including with support for academic research. But building and operating those datacenters is expensive. And the semiconductors – or graphical processing units (GPUs) – that are essential to power the servers for AI workloads remain costly and in short supply. Although governments and companies are working hard to fill the gap, doing so will take some time.
With this reality in mind, regulators around the world are asking important questions about who can compete in the AI era. Will it create new opportunities and lead to the emergence of new companies? Or will it simply reinforce existing positions and leaders in digital markets?
I am optimistic that the changes driven by the new AI era will extend into the technology industry itself. After all, how many readers of this paragraph had, two years ago, even heard of OpenAI and many other new AI entrants like Anthropic, Cohere, Aleph Alpha, and Mistral AI? In addition, Microsoft, along with other large technology firms are dynamically pivoting to meet the AI era. The competitive pressure is fierce, and the pace of innovation is dizzying. As a leading cloud provider and an innovator in AI models ourselves and through our partnership with OpenAI, we are mindful of our role and responsibilities in the evolution of this AI era.
Throughout the past decade, we’ve typically found it helpful to define the tenets – in effect, the goals that guide our thinking and drive our actions as we navigate a complex topic. We then apply these tenets by articulating the principles we will apply as we make the decisions needed to govern the development and use of technology. I share below the new tenets on which we are basing our thinking on this topic, followed by our 11 AI Access Principles.
Our AI Access Tenets
Fundamentally, there are five tenets that define Microsoft’s goals as we focus on AI access, including our role as an infrastructure and platforms provider.First, we have a responsibility to enable innovation and foster competition. We believe that AI is a foundational technology with a transformative capability to help solve societal problems, improve human productivity, and make companies and countries more competitive. As with prior general-purpose technologies, from the printing press to electricity, railroads, and the internet itself, the AI era is not based on a single technology component or advance. We have a responsibility to help spur innovation and competition across the new AI economy that is rapidly emerging.
AI is a dynamic field, with many active participants based on a technology stack that starts with electricity and connectivity and the world’s most advanced semiconductor chips at the base. It then runs up through the compute power of the public cloud, public and proprietary data for training foundation models, the foundation models themselves, tooling to manage and orchestrate the models, and AI-powered software applications. In short, the success of an AI-based economy requires the success of many different participants across numerous interconnected markets.
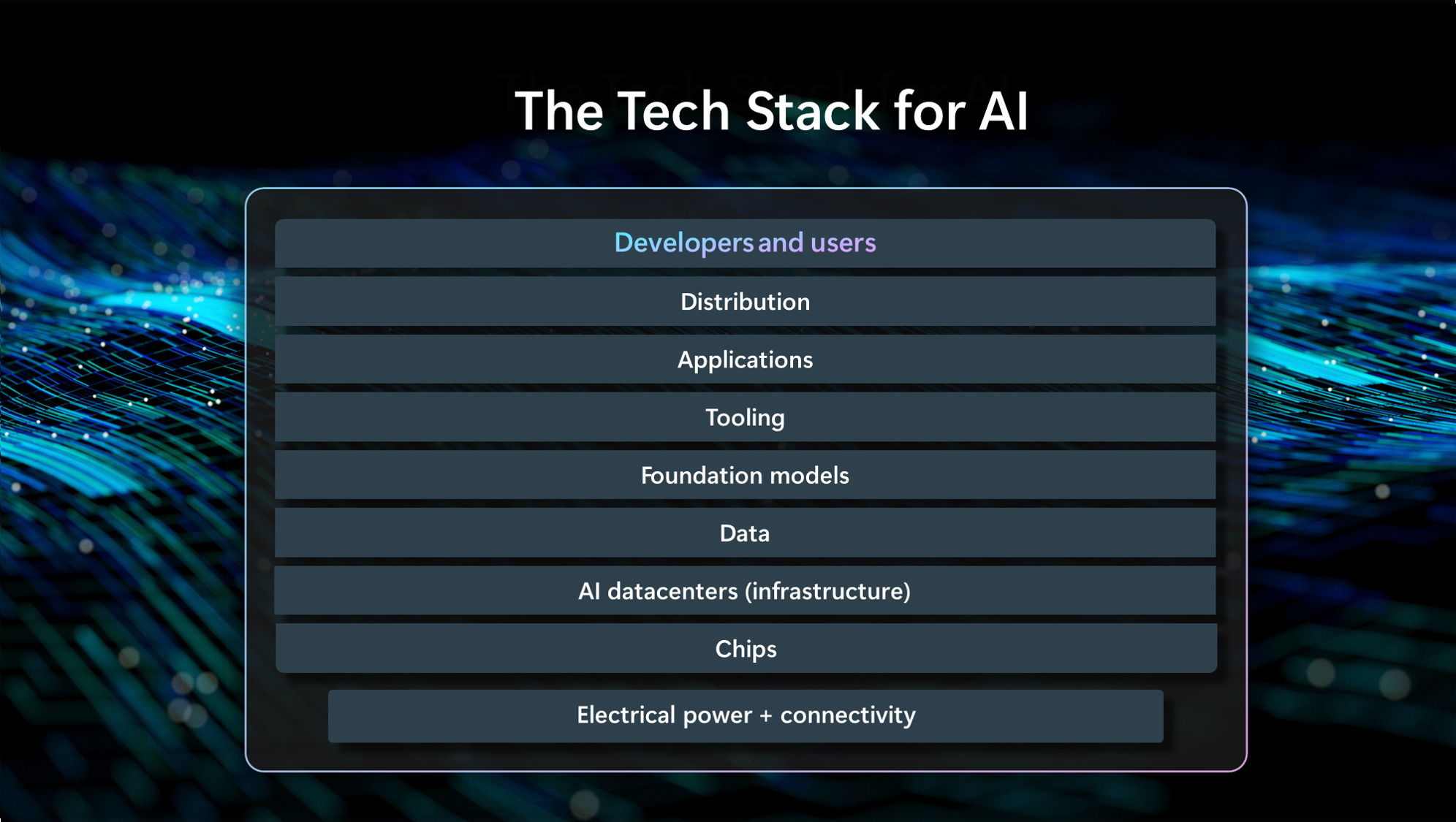
You can see here the technology stack that defines the new AI era. While one company currently produces and supplies most of the GPUs being used for AI today, as one moves incrementally up the stack, the number of participants expands. And each layer enables and facilitates innovation and competition in the layers above. In multiple ways, to succeed, participants at every layer of the technology stack need to move forward together. This means, for Microsoft, that we need to stay focused not just on our own success, but on enabling the success of others.
Second, our responsibilities begin by meeting our obligations under the law. While the principles we are launching today represent a self-regulatory initiative, they in no way are meant to suggest a lack of respect for the rule of law or the role of regulators. We fully appreciate that legislators, competition authorities, regulators, enforcers, and judges will continue to evolve the competition rules and other laws and regulations relevant to AI. That’s the way it should be.
Technology laws and rules are changing rapidly. The European Union is implementing its Digital Markets Act and completing its AI Act, while the United States is moving quickly with a new AI Executive Order. Similar laws and initiatives are moving forward in the United Kingdom, Canada, Japan, India, and many other countries. We recognize that we, like all participants in this new AI market, have a responsibility to live up to our obligations under the law, to engage constructively with regulators when obligations are not yet clear, and to contribute to the public dialogue around policy. We take these obligations seriously.
Third, we need to advance a broad array of AI partnerships. Today, only one company is vertically integrated in a manner that includes every AI layer from chips to a thriving mobile app store. As noted at a recent meeting of tech leaders and government officials, “The rest of us, Microsoft included, live in the land of partnerships.”
People today are benefiting from the AI advances that the partnership between OpenAI and Microsoft has created. Since 2019, Microsoft has collaborated with OpenAI on the research and development of OpenAI’s generative AI models, developing the unique supercomputers needed to train those models. The ground-breaking technology ushered in by our partnership has unleashed a groundswell of innovation across the industry. And over the past five years, OpenAI has become a significant new competitor in the technology industry. It has expanded its focus, commercializing its technologies with the launch of ChatGPT and the GPT Store and providing its models for commercial use by third-party developers.
Innovation and competition will require an extensive array of similar support for proprietary and open-source AI models, large and small, including the type of partnership we are announcing today with Mistral AI, the leading open-source AI developer based in France. We have also invested in a broad range of other diverse generative AI startups. In some instances, those investments have provided seed funding to finance day-to-day operations. In other instances, those investments have been more focused on paying the expenses for the use of the computational infrastructure needed to train and deploy generative AI models and applications. We are committed to partnering well with market participants around the world and in ways that will accelerate local AI innovations.

Fourth, our commitment to partnership extends to customers, communities, and countries. More than for prior generations of digital technology, our investments in AI and datacenters must sustain the competitive strengths of customers and national economies and address broad societal needs. This has been at the core of the multi-billion-dollar investments we recently have announced in Australia, the United Kingdom, Germany, and Spain. We need constantly to be mindful of the community needs AI advances must support, and we must pursue a spirit of partnership not only with others in our industry, but with customers, governments, and civil society. We are building the infrastructure that will support the AI economy, and we need the opportunities provided by that infrastructure to be widely available.
Fifth, we need to be proactive and constructive, as a matter of process, in working with governments and the IT industry in the design and release of new versions of AI infrastructure and platforms. We believe it is critical for companies and regulators to engage in open dialogue, with a goal of resolving issues as quickly as possible – ideally, while a new product is still under development. For our part, we understand that Microsoft must respond fully and cooperatively to regulatory inquiries so that we can have an informed discussion with regulators about the virtues of various approaches. We need to be good listeners and constructive problem solvers in sorting through issues of concern and identifying practical steps and solutions before a new product is completed and launched.

Our AI Access Principles
The foregoing tenets come together to shape the new principles we are announcing below. It’s important to note that, given the safety, security, privacy, and other issues relating to responsible AI, we need to apply all these principles subject to objective and effective standards to comply with our legal obligations and protect the public. These are discussed further below. Subject to these requirements, we are committed to the following 11 principles: Read more:

Microsoft’s AI Access Principles: Our commitments to promote innovation and competition in the new AI economy - Microsoft On the Issues
As we enter a new era based on artificial intelligence, we believe this is the best time to articulate principles that will govern how we will operate our AI datacenter infrastructure and other important AI assets around the world. We are announcing and publishing these principles – our “AI...