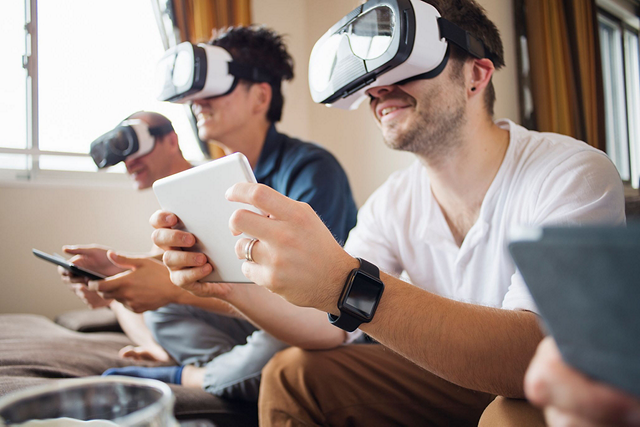
Gaming industry revenue is estimated to have exceeded $208 billion in 20221. In the U.S. alone, approximately 165 million people play video games, averaging 24 hours per week on their electronic devices, ranging from personal computers and laptops to mobile phones. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) headset usage is significantly on the rise, with more than 25% of gamers planning to obtain a headset in the next 12 months.
Wi-Fi is continuously improving with each generation and the addition of dual band simultaneous (DBS) in Wi-Fi 6 improved latency significantly. However, the continuous evolution of games require superior internet connections that can meet today’s demanding gaming requirements: reliable low latency, consistent high throughput and minimal jitter. And now, the introduction of Wi-Fi 7 brings innovative technologies into the mix that can alleviate these concerns.
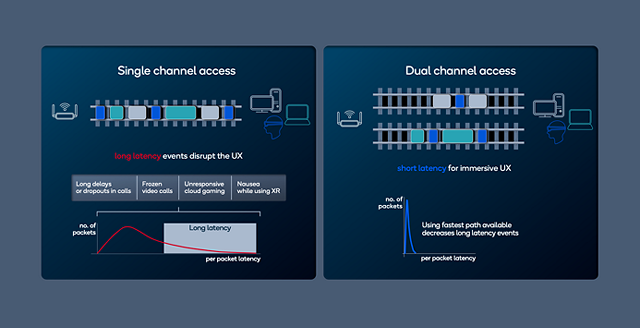
Figure 1: Latency comparison based on throughput in a Wi-Fi 7 and a pre-Wi-Fi 7 system.
What are these new Wi-Fi 7 technologies?
The Wi-Fi 7 specification was developed at Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, in the 802.11be work group where it was known as Extremely High Throughput (EHT), to significantly push the performance boundary into spheres that enable gamers and content creators to untether themselves from wired connections. Wi-Fi 7 benefits from multiple areas of improvement including:
Enabling multi-Gigabit throughput while maintaining the lowest possible latency and jitter is crucial for online gaming and XR applications, where poor latency and jitter performance can lead to lag, sub-par results, non-immersive gaming experiences and even nausea in VR.
- Faster connections through wider channel bandwidth and advanced modulation.
- Adaptive connections, which form a wider bandwidth cannel around interference.
- The ability to create multiple connections in a flexible manner.
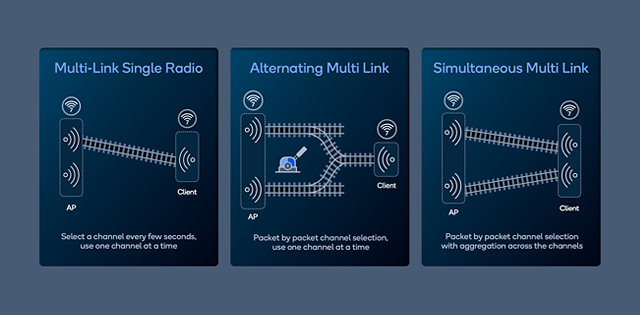
Figure 2: Wi-Fi 7 Multi-Link operation options.
Wi-Fi 7 enables higher throughput and lower latency
Wi-Fi 7’s lower latency and higher throughput benefit simultaneously from new features, such as:
- Multi-Link operation, which — depending on the capability of the device — enables a client to utilize the multiple radios in a router in various ways: switch easily between the channels as needed, switch between channels on a packet by packet decision and aggregate two independent channels into an effective channel up to 320 megahertz (MHz) wide (Figure 2).
- Wider channels of up to 320 MHz bandwidth and higher packet density of 4K Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM), increasing the likelihood of an available timeslot to transmit data packages earlier than in a system with less bandwidth. This achieves up to 5.8 Gbps — 2.4 times the peak throughput of a Wi-Fi 6/6E connection.
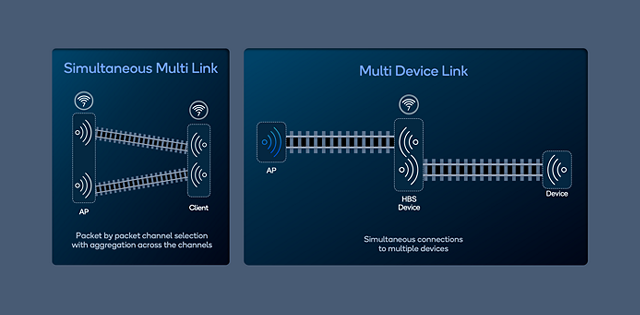
Figure 3: Wi-Fi 7 HBS Multi-Link operation.
High Band Simultaneous Multi-Link takes Wi-Fi to a new level
Qualcomm Technologies’ implementation of High Band Simultaneous (HBS) is designed to enable clients to connect to an access point (AP) with an effective bandwidth of up to 320 MHz even if a contiguous 320 MHz channel is unavailable. HBS Multi-Link can aggregate 160 MHz + 160 MHz channels in the five and six MHz bands to an effective 320 MHz bandwidth using simultaneous Multi-Link. This brings the latency advantages from dual channel access (Figure 1) at the high throughput obtained by aggregating two High Band radios from your router.
In addition, HBS Multi-Link enables multi-device connections using separate radios to connect to an AP and to another device such as a head-mounted display (HMD) or others simultaneously (Figure 3).
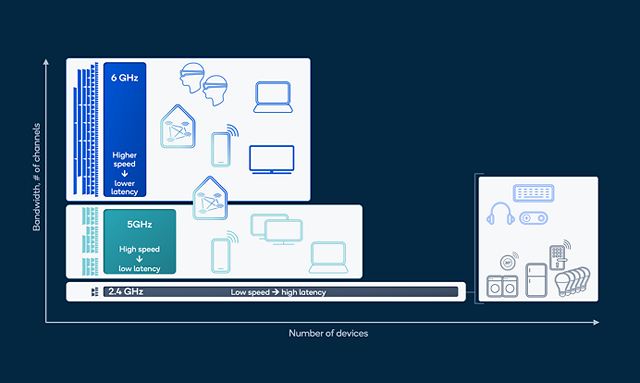
Figure 4: IoT edge and high throughput devices distributed over different Wi-Fi bands.
Selecting the right bands for the right purpose
By moving high-throughput and latency-critical application into the high bands, HBS Multi-Link technology reduces traffic within the widely used 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band. Gamers will often use a Bluetooth-attached headset or speakers, which also use 2.4 GHz. Moving Wi-Fi to the High Bands frees up 2.4GHz for the high-quality immersive sound on Bluetooth. It is also designed to improve throughput and reduces latency for the remaining 2.4 GHz peripherals and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Examples of typical 2.4 GHz spectrum-connected devices are depicted in Figure 4.
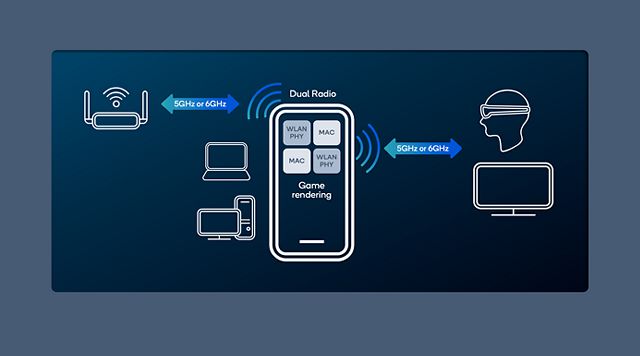
Figure 5: Wi-Fi 7 HBS Multi-link, multi-device operation connecting a client to an AP and to an HMD.
How does Wi-Fi 7 result in superior gaming experiences?
Another major improvement related to the HBS Multi-Link capability of Wi-Fi 7 is the ability to establish simultaneous high-throughput links to different devices (Figure 5), which provides high-throughput connections to enjoy distributed compute XR gaming experiences. This, for example, would allow the use of an XR or HMD device without the physical restraints of cables. For PC-connected VR (PCVR) gaming, an HBS-capable PC can connect directly to a VR HMD and the router, using the High Bands for each.
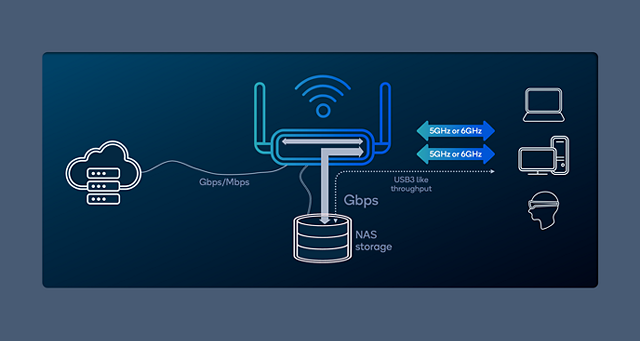
Figure 6: Wi-Fi 7 AP with ethernet connected NAS.
Wi-Fi 7 untethers gaming and storage devices
With Wi-Fi 7, it is now possible to achieve a wire-like performance using untethered external network-attached storage (NAS) devices for storage expansion, while simultaneously using the same connection for gaming (Figure 6). Gamers and content creators directly benefit from the significant increase in usable channel bandwidth and flexible link selection provided by the new features of Wi-Fi 7. Furthermore, it is now possible to add NAS devices or external drives to offload often large scene libraries, while also continuously recording a game screen with minimum compression for future content sharing — all performed wirelessly.
When a Wi-Fi 7-connected NAS is performing similar to local storage, content creators can store recordings and develop content, eliminating the need to move around huge video files for editing.
Source:

Wi-Fi 7 has arrived: Here’s exactly what that means for gaming
Low latency and multi-Gigabit throughput powered by new Wi-Fi 7 tech enable untethered gaming and content creation.